C Move

Returns an rvalue reference to arg.
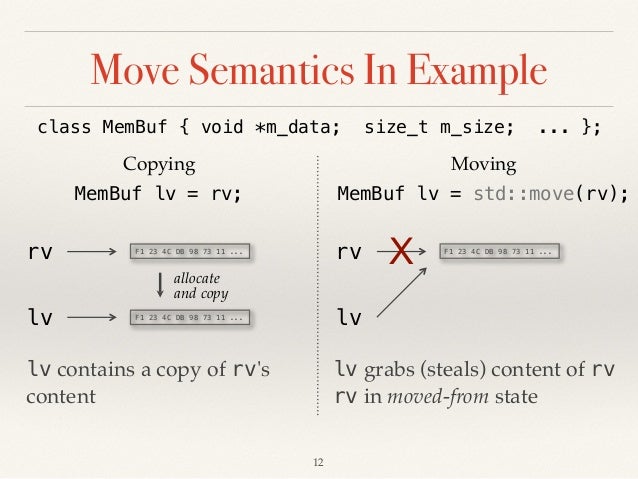
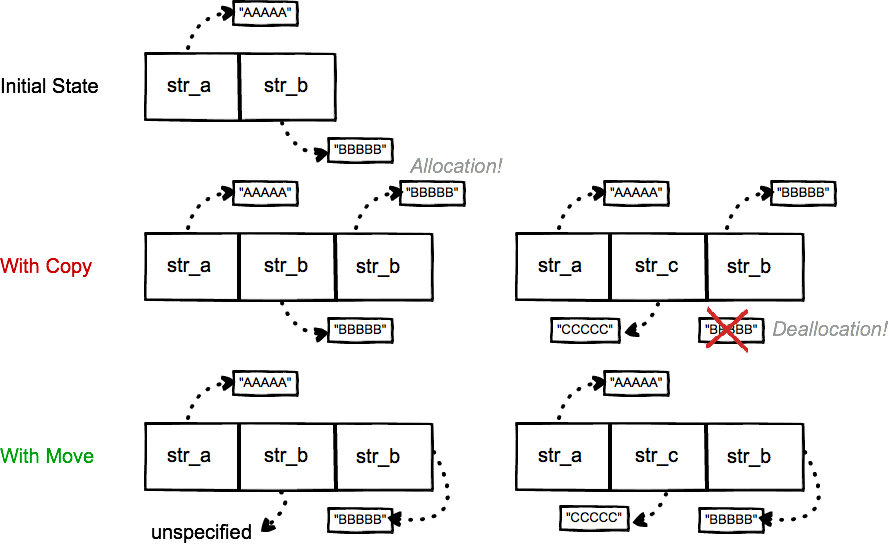
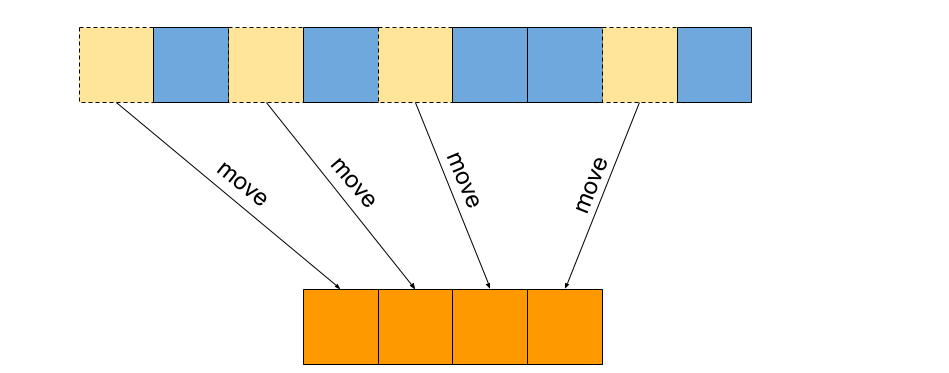
C move. While move constructors work on the r value references and move semantics move semantics involves pointing to the already existing object in the memory. The value of the elements in the first last is transferred to the elements pointed by result. For example a move constructor of a linked list might copy the pointer to the head of the list and store nullptr in the argument instead of allocating and copying individual nodes. The move assignment operator is called whenever it is selected by overload resolution e g.
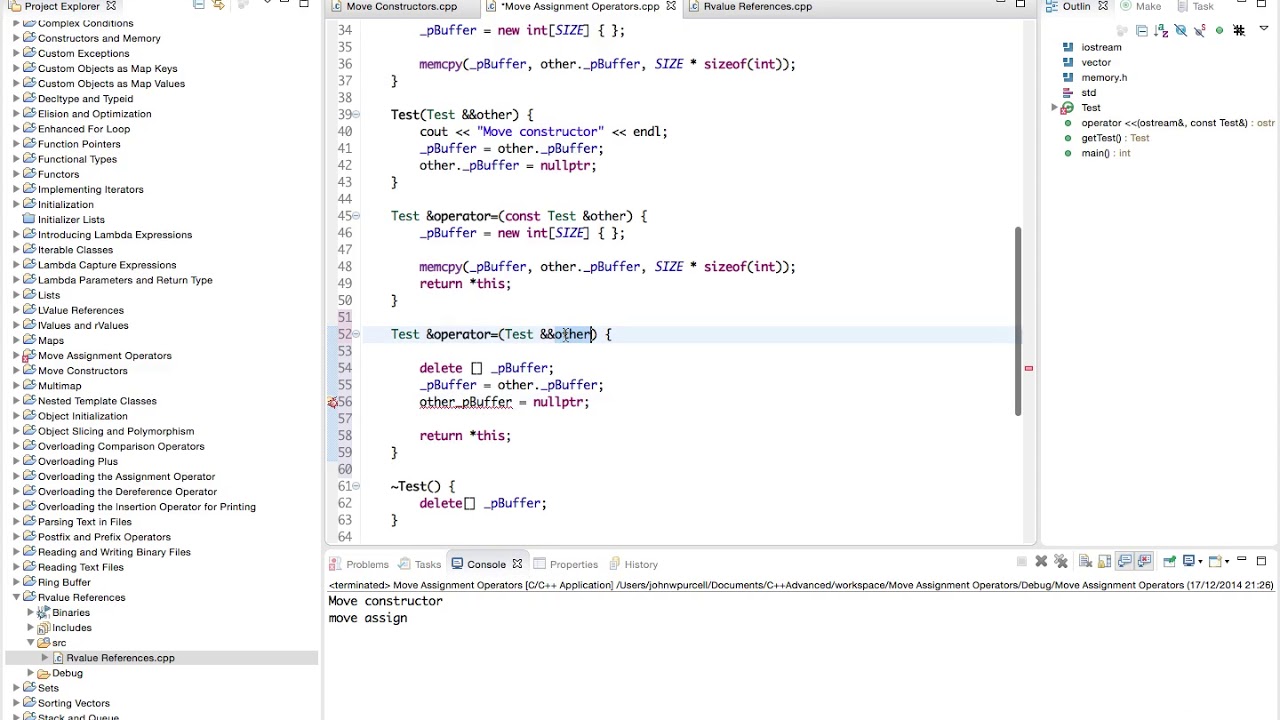
After the call the elements in the range first last are left in an unspecified but valid state. A move constructor enables the resources owned by an rvalue object to be moved into an lvalue without copying. And in addition to copy assignment operators they have move assignment operators the move constructor is used instead of the copy constructor if the object has type rvalue reference type. C のstd move とは 引数で与えられたオブジェクトの持つリソースを左辺へオブジェクトに移動する機能を提供します 所有権を移動します std moveは c 11で追加されました std moveは キャストの1つです.
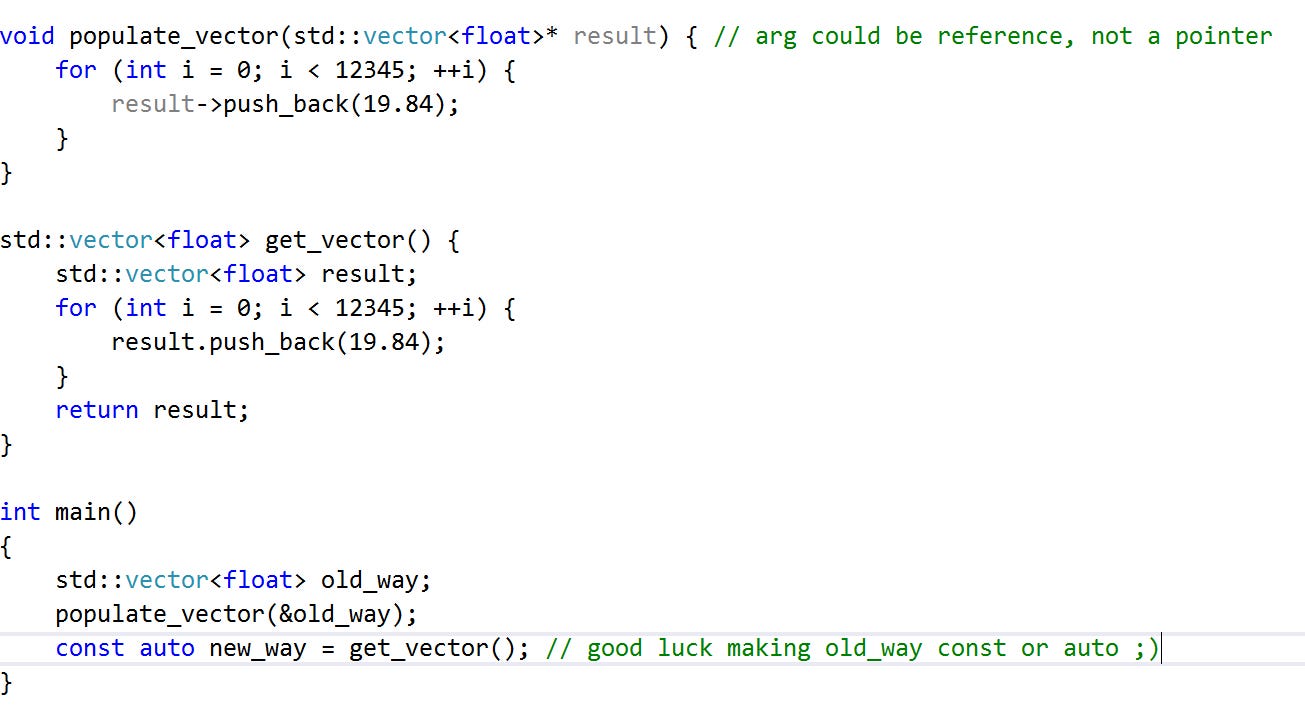
If the argument identifies a resource owning object these overloads have the option but aren t required to move any resources held by the argument. On declaring the new object and assigning it with the r value firstly a temporary object is created and then that temporary object is used to assign the values to the object. For more information about move semantics see rvalue reference declarator. When an object appears on the left hand side of an assignment expression where the right hand side is an rvalue of the same or implicitly convertible type.
Generally rvalues are values whose address cannot be obtained by dereferencing them either because they are literals or because they are temporary in nature such as values returned by functions or. Move range of elements moves the elements in the range first last into the range beginning at result. This topic describes how to write a move constructor and a move assignment operator for a c class.